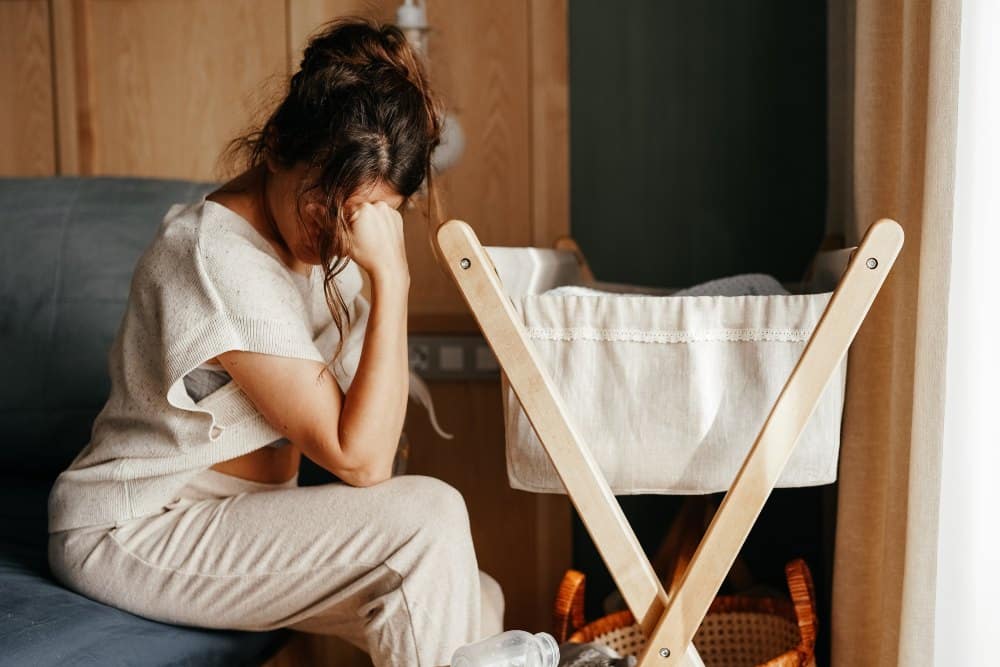
Becoming a mother is an experience like no other, but it can also be filled with a range of emotions, from elation to anxiety and exhaustion. The postpartum period is often characterized by feelings of exhaustion, anxiety, and mood swings. While these emotions are a natural part of the new motherhood experience, you have to recognize when they become more than just passing feelings and become something else– postpartum depression. A mental health condition that affects around 1 in 7 mothers in the United States.
Postpartum depression can feel like a never-ending storm cloud, obscuring the joys of motherhood and even have ripple effects on your family’s well-being. While it’s a serious issue, it’s also treatable, and help is available. In this article, we’ll define postpartum depression, explore its signs and symptoms and discuss how it differs from regular depression. We’ll also provide a useful guide on how to seek help if you think you may be experiencing it.
What is Postpartum Depression?
Postpartum depression (PPD), also called baby blues, is a type of depression that can develop after childbirth, typically within the first few weeks or months. This condition is complex, may arise from a myriad of physical, emotional, hormonal, and social factors, and can affect any new mother, regardless of her age, race, or socioeconomic status.
Battling with the ups and downs of motherhood comes as expected for many mothers. However, for new moms with postpartum depression, the rollercoaster can feel like a brutal and endless ride that lasts long after the baby is born. This can often interfere with daily functioning and bonding with the baby. That said, PPD is also treatable and many women recover with the right support and treatment.
Signs of Postpartum Depression
Postpartum depression often presents itself differently among mothers and the best way to tell for sure is to consult your doctor. However, there are some common signs and symptoms to look out for.
Here are some common symptoms of postpartum depression:
- A prolonged feeling of sadness, despair, or hopelessness that lasts for at least two weeks.
- A lack of interest or pleasure in activities that were once enjoyable, including spending time with loved ones or engaging in hobbies.
- A short fuse, or feelings of frustration or anger, even over minor things.
- Trouble sleeping or excessive sleeping.
- Worry, panic, and fear can sometimes feel overwhelming.
- Fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and a general lack of energy.
- Changes in appetite, such as an increase or decrease in appetite and weight changes.
- Difficulty bonding with the baby, including feelings of detachment, lack of interest, or a lack of love towards the baby.
- Feeling disconnected from caring for your baby.
- Distancing yourself from family members and loved ones.
- Feeling overwhelmed by the demands of motherhood or daily life.
- Thoughts of harming yourself or the baby.
Postpartum depression is a common and treatable condition and there’s no cause to worry if you are experiencing any of these symptoms.
Depression vs. Postpartum Depression
Depression and postpartum depression are both mood disorders that impact a person’s mental and emotional well-being. Although they share similarities, there are key differences between the two. Depression can occur at any time, while postpartum depression specifically affects new mothers within the first year after childbirth. This is due to hormonal changes during and after pregnancy that can contribute to postpartum depression.
Secondly, the causes of depression are varied and can include genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. In contrast, postpartum depression is believed to be caused by hormonal changes during and after pregnancy.
Postpartum depression is often accompanied by physical symptoms such as fatigue, insomnia, and appetite changes. These symptoms may not be as pronounced in cases of depression that are not related to childbirth.
Finally, treatment for postpartum depression may involve medication and therapy specifically tailored to new mothers, while treatment for depression may involve various therapies and medications, depending on the individual case.
Common Postpartum Depression Treatment
With the right interventions, women with postpartum depression can experience significant improvements in their mental health and overall quality of life. Below are several proven approaches for treating postpartum depression:
Psychotherapy
Talk therapy as a treatment for postpartum depression is highly effective. By working with a mental health professional, mothers can explore their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in a safe and supportive environment. This helps them uncover the underlying causes of their depression and develop ways of dealing with them.
Medication
Antidepressants can be prescribed to help treat PPD. These medications work by altering the levels of neurotransmitters in the brain to help regulate mood. It’s best practice to work closely with a healthcare provider to find the right medication and dosage, as well as to monitor any potential side effects.
Support Groups
Becoming a member of a support group can provide postpartum depressed women the sense of belonging and connection they need. Support groups may be led by a mental health professional or run by peers and provide a space to connect with others who are going through similar experiences.
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can also help manage PPD. Getting enough sleep, eating a good diet, and exercising frequently can all help elevate mood and lessen stress. Women with PPD may also benefit from practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga.
Self-Care
Self-care is an important component of treating postpartum depression. Taking time for oneself and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation can help women feel more balanced and energized. Self-care may involve setting boundaries, asking for help, and engaging in activities that promote self-growth and self-compassion.
When to Seek Out Professional Assistance for Postpartum Depression
You need to seek professional medical help when:
- The symptoms last longer than two weeks.
- You are unable to handle daily challenges or function regularly.
- You’re contemplating doing something bad to your child or yourself.
- The majority of the day is spent with intense anxiety, fear, and panic.
Help is Available at D’Amore Mental Health
D’Amore Mental Health offers a variety of therapies to support new mothers going through postpartum depression. Our team of skilled healthcare providers offers talk therapy and medication management to help you develop a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
We understand the challenges of postpartum depression and how it can impact your quality of life and how you relate with your newborn. Our supportive and understanding environment provides a safe space for you to work through your emotions and develop effective coping strategies.
Our services are backed by years of experience and the latest research, ensuring that you receive the best possible care. Don’t struggle with postpartum depression alone – reach out to us for the support you need to get back on track.
Contact us to learn more about our mental health services for postpartum depression.